How to reach new markets by testing new ideas

At stake was the existence of almost 900 small business owners. In a company owned by a member association, there is not a large fund to pour money from, and to compromise guarantee salaries and other soft values that make Taxi Stockholm unique in the market was not the solution. While Taxi Stockholm and all the owner companies were fighting for their lives, the marketing department tried to do everything they could to find a market to communicate with.
Digital Wellness - five abilities to lean on
So how did we proceed? The situation they were in was completely new to everyone involved, so it was extra important to use models and methods that could create security and structure. At Esatto, we have been working with the concept of Digital Wellness for several years. The concept includes five capabilities that we believe future organizations need to develop:
Customer: How do we switch to a customer-driven business?
Agil: How do we change our organization?
Flex: How do we create high technical flexibility?
Data: What does our value machinery by means of data look like?
Since the usual taxi ride was completely stationary, Taxi Stockholm needed to generate new revenue, so the focus was on rapid market innovation.
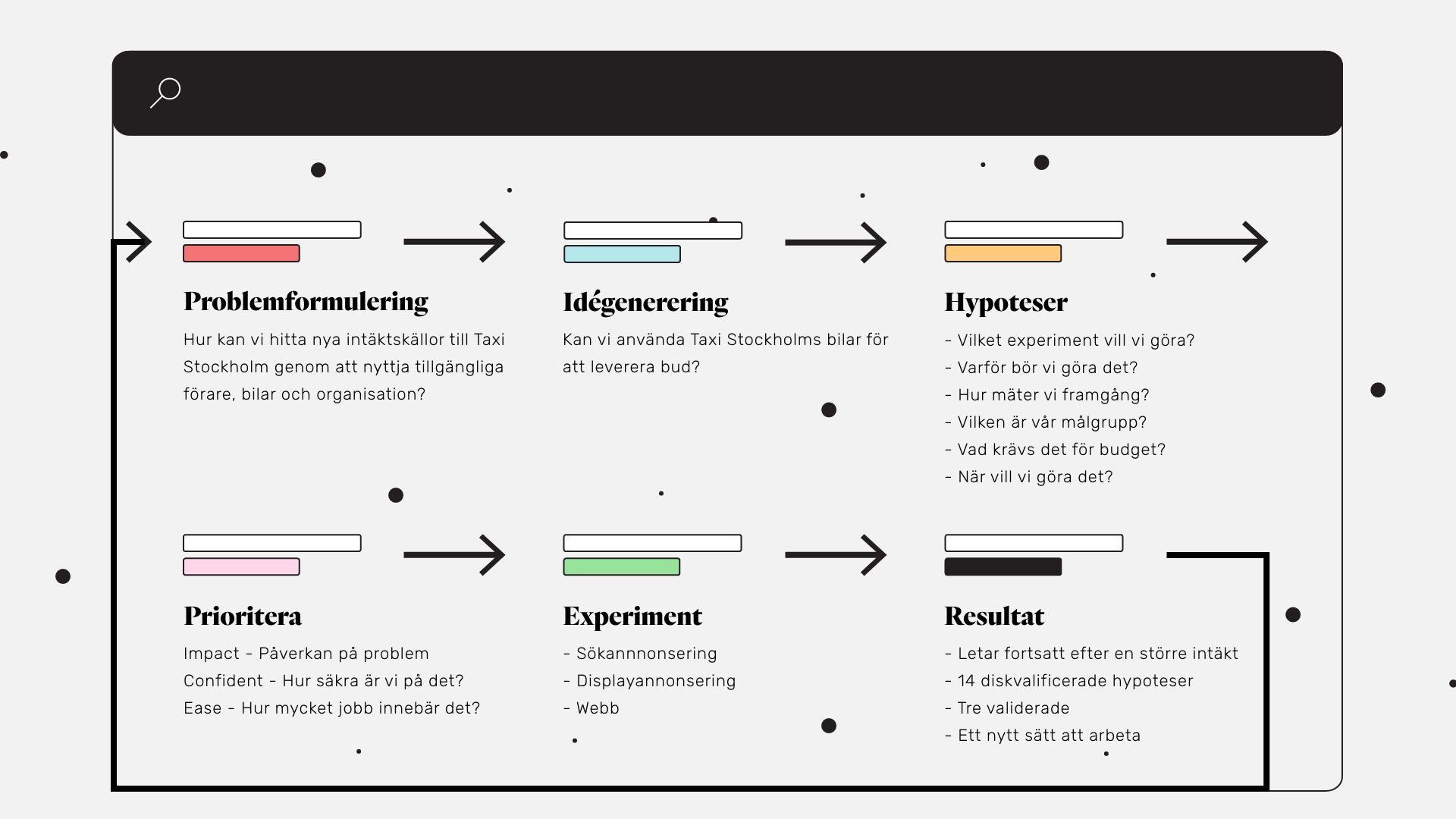
We piled up the work based on five parts:
- Problem formulation
- Idea generation
- Hypothesis formulation
- Prioritization
- Experimentation
Problem statement
To understand the problem you are facing is an important first step. Here it’s easy to get lost, especially when you’re facing a crisis. This work can be extremely extensive and include different types of data collection, in-depth interviews, market analyzes and priorities.
It is important to know what problem you are facing to be able to start generating ideas. We needed to pause and first find out what we it is we were trying to solve. This phase is often rushed past and instead you start thinking about ideas and will hunt you later in the process.
The challenge is important because it is the guide in our learnings. Even if we just want to solve the problem, the process is actually more important. By starting to look from the perspective of the problem we can learn during the process.

Brainstorming
Many organizations already have a lot of experience in this area. An important part here is that we generate ideas with one and the same method over time, so the organization becomes secure in the way how to do it. It is important that we set the conditions and rules that exist and how we collaborate to build on each other's ideas. In addition, we need to have different perspectives, the more the better, from different departments with different skills. We also need to stick to the problem statement. That is what we should solve in this crisis, nothing else.
In the brainstorming with Taxi Stockholm, there were plenty of good ideas, from collaborations with local producers for home delivery of their products and collaborations with hotels and conference facilities for "package travel" that includes a taxi journey, to increasing the degree of return travel through more active work in the app.
Formulate hypotheses
A hypothesis is a framework for formulating an idea. It can be anything from "I think this will lead to that", to a hypothesis structure that is a page long. It is often quite good to set it somewhere in between the two. The most important thing is to find a way to build hypotheses that work for your organization, so that hypotheses are always built in the same way. This mean that we start thinking hypotheses-driven from the beginning. In addition, a good hypothesis framework forces one to think through all aspects of one's idea and find challenges and shortcomings with it. It is also through the hypothesis that we formulate what success is, how should we test this idea and when is it so successful that we should take it further.
Prioritize hypotheses
The next step is to find out what we are going to prioritize to do first. All the ideas that we have cannot be implement at once, so we need to prioritize them. Here, the hypotheses are prioritized against each other and it’s best to gather the whole team sits together. Prioritization is one of the most difficult things we can do and therefore it is important that we formalize it.
One important thing when we prioritize is that we use the same model over time, so that we continually improve it. When working with Taxi Stockholm, we used the ICE model, it’s a simple and easy model to use. ICE simply means that we score: Impact, Confidence, Ease - the idea with the highest score gets the highest priority.
Mandate, anchoring and support from management and the rest of the organization is crucial for the whole process, but it is often somewhere here a challenge can emerge. The challenge is often that time, energy and budget are needed for something that cannot be specified more than "we want to spend a lot of money on something that has an uncertain income".
And it needs to be allowed to be so vaguely specified. Our experience is that the pandemic has given us some space in these issues, we have to do something and this is not a particularly bad plan - even if it has uncertainty factors attached to it.
Start the experiment
An experiment can be anything from an AB-test on the web or a function in the app, to a search ad on Google or a display ad on Facebook. It should be able to validate or disqualify our hypothesis in the simplest possible way. Regardless result, we must have learned something that is of valuable for the organization. That should be the starting point. This means that the experiment needs to be designed according to the hypothesis. In some cases, this may mean that the experiment is a smaller variant of a package that we want to test, or we seek market validation before we build new functionality on our website. It’s important that we design the experiment so that it can answer the right question.
Because we were chasing fast market innovation, we put a little extra emphasis on ease (easy to create), because we were in such an extremely vulnerable situation. We wanted to get as many answers as possible as quickly as possible. This meant that experiments that were easy to validate or disqualify were moved up the list.
Some of our ideas were about packaging existing product to new target groups, then the experiment was quite similar to the campaign that we would release with validated results. In some cases, our ideas were more complex because the experiment aimed to validate the hypothesis against the market. We wanted to know if this was interesting for the target group before we put a lot of time, energy, and money into the idea. It is important to be vigilant about the differences all the way from hypothesis to experiment.
To take a result further
As we talked about above, it is important not only to see successful results in for example, a taxi booking. It's about learning, to actually create movement forward. New energy and new ways of working will be created if we work in this way, and that is what is important. Because if we succeed in that, we will also succeed in our goal.
We want a result, a response to a hypothesis, to guide the organization further. We have received an answer to a question and if that answer was validating, we will grow that business or that direction. It can be about building functionality into the app, about formalizing and scaling up collaborations with different types of partners or completely new services that are to be rolled out in the organization. In the same way, a disqualified hypothesis should teach us something and guide us further in the work with future ideas and hypotheses. And it’s important that we are skilled thorough this process so that the results of the experiment are exactly as valuable as it could be.

